
It consists of summing the gross value added of all industries in the country. These are the income approach, the expenditure approach and the production approach. One way of thinking about it is to think of the GDP as a cake and the population determines the number of slices you have to cut the cake into – the GDP per capita is the size of the slice. For example, two countries may have a similar GDP but if one has three times the population of the other the same amount has to be shared out among three times as many people as smaller slices of cake. As global economies evolve, GDP’s significance persists, with ongoing discussions and enhancements to Certified Bookkeeper ensure it continues to reflect economic realities accurately. Despite these limitations, GDP remains an indispensable tool in macroeconomic analysis.
- Distinctions must be kept in mind between quantity and quality of growth, between costs and returns, and between the short and long run.
- There are many different ways to measure a country’s GDP, so it’s important to know all the different types and how they are used.
- You may also want to follow GDPNow and the Nowcasting Report to see how GDP may be shaping up before the next official release.
- Put simply; gross domestic product is the sum of all economic activity in a country over a specific period.
- For economists, a country’s GDP reveals the size of the economy but provides little information about the standard of living in that country.
- It thereby introduced the HDI in 1990 to take other factors into account and provide a more well-rounded evaluation of human development.
How is GDP used as a reference?
Instead, it assesses all domestically produced goods and services based on current market prices. Furthermore, it is an excellent tool for comparing economic output from different quarters of the same year. GDP or gross domestic product is the total value of goods and services generated inside a country over an accounting period. In simpler words, it reflects a nation’s total domestic production and foreign balance of trade.
📆 Date: June 28-29, 2025🕛 Time: 8:30-11:30 AM EST📍 Venue: OnlineInstructor: Dheeraj Vaidya, CFA, FRM

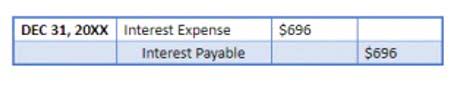
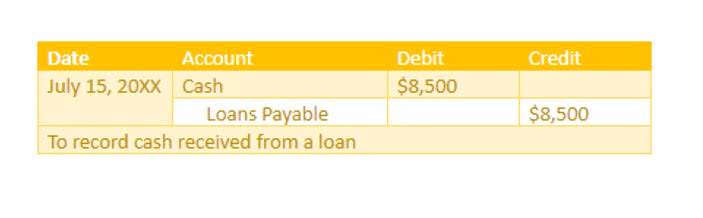
The term real in real income merely reflects the income after inflation has been subtracted from the figure. Last, the difference between a country’s exports and imports Certified Public Accountant is called net imports. Net exports reflect a country’s competitiveness in international markets as how well a country may leverage global markets for expansion. Investment encompasses spending on capital goods, such as machinery, equipment, and infrastructure. When a country spends on investment, it has the aim of increasing future production capacity. Policymakers, businesses, and institutions use GDP to make key economic decisions.
Why Is Real GDP More Accurate Than Nominal GDP?
There are three different approaches for calculating GDP which is used by economists. As an investor in a rising GDP environment, your portfolio might benefit from loading up on high-growth stocks rather than bonds. You’ll also have to decide on the size of your stock positions, whether to buy more or less, for how long, and in which sectors of the broader market. GDP reports, published by the BEA, are estimated on a quarterly and annual basis, although statistics are released each month.
Measuring National Income (GDP)

There is a large gap between market and PPP-based exchange rates in emerging market and developing economies. These differences mean that emerging market and developing economies have a higher estimated dollar GDP when gross economics definition the PPP exchange rate is used. One of the most common is GDP, which stands for gross domestic product.
Economies are sometimes in periods of boom, and sometimes periods of slow growth or even recession (with the latter sometimes defined as two consecutive quarters in which output declines). In the United States, for example, there were 10 recessions of varying length and severity between 1950 and 2017 (see chart). The National Bureau of Economic Research makes the call on the dates of US business cycles. Consider a country that has a gross national product that exceeds its gross domestic product. This indicates that its citizens, businesses, and corporations are providing net inflows to the country through their overseas operations.
- It also assists in assessing the growth, expansion, contraction, or decline of an economy.
- In the United States, the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) calculates real GDP from year-to-year by factoring in a price deflator.
- The group states it is feasible because the COVID-19 Delta variation has less influence in Italy, and economic indicators have been greater than projected.
- Real GDP accounts for changes in market value and thus narrows the difference between output figures from year to year.
- The U.S. was the world’s largest economy in 2024 according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
The GDP price deflator is considered to be a more appropriate inflation measure for measuring economic growth than the consumer price index (CPI) because it isn’t based on a fixed basket of goods. Government spending refers to the expenditure by governments on goods and services. This can range from public education and healthcare to defense and infrastructure projects. While government spending contributes directly to nominal GDP, its impact on the economy can vary depending on the nature of the expenditure.
